Home
A comprehensive resource for safe and responsible laser use
US: New federal law makes aiming laser at watercraft a felony
23 Jan 2021 -- Categories: Bans & Restrictions | Laws | Ways to reduce incidents | Commentary from LPS.com | SLA news
A new federal law makes it illegal "to cause the beam of a laser pointer to strike a vessel operating on the navigable waters of the United States." The vessels include Coast Guard patrol boats, ferries, merchant ships and small watercraft.
The provision was added as part of the National Defense Authorization Act for FY2021, which became law on January 1 2021. It will be added to Title 46 United States Code, Chapter 700, Subchapter II, section 70014 entitled "Aiming laser pointer at vessel."
The law lists exceptions: "This section shall not apply to a member or element of the Department of Defense or Department of Homeland Security acting in an official capacity for the purpose of research, development, operations, testing, or training."
It also defines laser pointer as follows: "In this section the term `laser pointer' means any device designed or used to amplify electromagnetic radiation by stimulated emission that emits a beam designed to be used by the operator as a pointer or highlighter to indicate, mark, or identify a specific position, place, item, or object.''
According to the U.S. Coast Guard Investigative Service, "[o]ffenders who target a Coast Guard vessel with a laser pointer and harm an officer can receive up to $25,000 in civil fines, and criminal penalties can include up to 25 years imprisonment."
Text of the Enrolled Bill is available from Congress.gov. As of January 27, 2021 the text of the Public Law 116-283 has not been uploaded. Comments by the CGIS are from an article in The Maritime Executive.
COMMENTARY FROM LASERPOINTERSAFETY.COM
This is the maritime version of the February 2012 law prohibiting aiming laser pointers at aircraft, U.S.C. Title 18, Chapter 2, Sec. 39A. There are some interesting differences.
The 2021 maritime law prohibits a beam from striking a vessel on the navigable waters. The 2012 aviation law prohibits aiming at an aircraft or at the flight path of an aircraft. Apparently aiming at a maritime vessel would not be illegal unless it struck the vessel.
The 2021 maritime law has one exception, for the Defense or Homeland Security departments. The 2012 aviation law has four exemptions. The first is for FAA, aircraft manufacturers, and FAA-authorized persons doing research or flight tests. The second is identical to the 2021 DoD and DHS exemption. The third exemption is for persons using a laser emergency signaling device to send a distress signal. The fourth allows the Justice Department in consultation with the Department of Transportation to provide additional exemptions; these are not considered or allowed under the 2021 law.
Both laws, 2021 and 2012, have an identical definition of "laser pointer."
The provision was added as part of the National Defense Authorization Act for FY2021, which became law on January 1 2021. It will be added to Title 46 United States Code, Chapter 700, Subchapter II, section 70014 entitled "Aiming laser pointer at vessel."
The law lists exceptions: "This section shall not apply to a member or element of the Department of Defense or Department of Homeland Security acting in an official capacity for the purpose of research, development, operations, testing, or training."
It also defines laser pointer as follows: "In this section the term `laser pointer' means any device designed or used to amplify electromagnetic radiation by stimulated emission that emits a beam designed to be used by the operator as a pointer or highlighter to indicate, mark, or identify a specific position, place, item, or object.''
According to the U.S. Coast Guard Investigative Service, "[o]ffenders who target a Coast Guard vessel with a laser pointer and harm an officer can receive up to $25,000 in civil fines, and criminal penalties can include up to 25 years imprisonment."
Text of the Enrolled Bill is available from Congress.gov. As of January 27, 2021 the text of the Public Law 116-283 has not been uploaded. Comments by the CGIS are from an article in The Maritime Executive.
COMMENTARY FROM LASERPOINTERSAFETY.COM
This is the maritime version of the February 2012 law prohibiting aiming laser pointers at aircraft, U.S.C. Title 18, Chapter 2, Sec. 39A. There are some interesting differences.
The 2021 maritime law prohibits a beam from striking a vessel on the navigable waters. The 2012 aviation law prohibits aiming at an aircraft or at the flight path of an aircraft. Apparently aiming at a maritime vessel would not be illegal unless it struck the vessel.
The 2021 maritime law has one exception, for the Defense or Homeland Security departments. The 2012 aviation law has four exemptions. The first is for FAA, aircraft manufacturers, and FAA-authorized persons doing research or flight tests. The second is identical to the 2021 DoD and DHS exemption. The third exemption is for persons using a laser emergency signaling device to send a distress signal. The fourth allows the Justice Department in consultation with the Department of Transportation to provide additional exemptions; these are not considered or allowed under the 2021 law.
Both laws, 2021 and 2012, have an identical definition of "laser pointer."
Germany: Laser/aircraft incidents decline 12.4% compared to last year
There were 113 laser illuminations of aircraft reported in Germany during the first half of 2018, compared with 129 reports in the first half of 2017, according to Deutsche Flugsicherung, the German air traffic control company on September 22 2018. This is a decrease of 12.4%.
This decrease is despite a doubling of incidents at Frankfurt International Airport. In the first half of 2018 there were 22 laser illuminations versus only 11 during the same period in 2017.
Declines were reported at Munich, Hamburg and Stuttgart airports.
A spokesperson for the German pilots' union Vereinigung Cockpit seemed to indicate that increasing prosecutions were a cause of the drop from 2017 to 2018: "A few years ago, the laser attack was a hip prank for some young people. The perpetrators must now be aware that they are consistently prosecuted."
From DW.com reporting on a story from public broadcast service ARD. Thanks to Greg Makhov for bringing this to our attention.
This decrease is despite a doubling of incidents at Frankfurt International Airport. In the first half of 2018 there were 22 laser illuminations versus only 11 during the same period in 2017.
Declines were reported at Munich, Hamburg and Stuttgart airports.
A spokesperson for the German pilots' union Vereinigung Cockpit seemed to indicate that increasing prosecutions were a cause of the drop from 2017 to 2018: "A few years ago, the laser attack was a hip prank for some young people. The perpetrators must now be aware that they are consistently prosecuted."
From DW.com reporting on a story from public broadcast service ARD. Thanks to Greg Makhov for bringing this to our attention.
UK: NPAS says only 1.4% of laser perpetrators were prosecuted
22 Mar 2018 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Statistics | Finding perpetrators | Ways to reduce incidents | Laws | SLA news
From 2014 to March 2018, there were 279 incidents where lasers illuminated National Police Air Service helicopters. Of those, only three or four were prosecuted, according to the NPAS head of safety.
James Cunningham told Police Oracle in a March 21 2018 article that there were a number of reasons for the low prosecution rate, including being not being able to follow the laser perpetrator due to being focused on another job (e.g., completing the original mission).
Also, when lasers are pointed from a tower block area, the helicopter crew may not be able to locate the source.
In 2017 there were 67 incidents [not clear if this is NPAS only], compared with 70 in 2016 and 103 in 2015. Cunningham said the reduction is because NPAS is trying to locate and pursue laser perpetrators, and report the incidents as crime. He said the Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Bill being considered in Parliament is a “step in the right” direction that could lead to more prosecutions.
In December 2017, NPAS purchased laser-reducing glasses which can enable pilots to continue even when illuminated by laser light.
From Police Oracle
James Cunningham told Police Oracle in a March 21 2018 article that there were a number of reasons for the low prosecution rate, including being not being able to follow the laser perpetrator due to being focused on another job (e.g., completing the original mission).
Also, when lasers are pointed from a tower block area, the helicopter crew may not be able to locate the source.
In 2017 there were 67 incidents [not clear if this is NPAS only], compared with 70 in 2016 and 103 in 2015. Cunningham said the reduction is because NPAS is trying to locate and pursue laser perpetrators, and report the incidents as crime. He said the Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Bill being considered in Parliament is a “step in the right” direction that could lead to more prosecutions.
In December 2017, NPAS purchased laser-reducing glasses which can enable pilots to continue even when illuminated by laser light.
From Police Oracle
UK: New UK law provides stronger penalties, easier prosecution for aiming a laser at a vehicle
On May 10 2018, the Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Act gained Royal Assent. The new law makes it an an offense to shine or direct a laser beam towards a vehicle which dazzles or distracts, or is likely to dazzle or distract the person with control of the vehicle. The law applies to England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland.
The penalties for violations are up to five years imprisonment and an unlimited fine; these penalties take effect starting July 10 2018.
The law applies to laser beams aimed at aircraft, motor vehicles, trains, ships, hovercraft and other vehicles. A vehicle does not have to be moving at the time of offense; if the engine or motor is running then the law applies. Another provision makes it an offense to shine or direct a laser beam towards an air traffic facility, or a person providing air traffic services, under the condition where the beam dazzles or distracts, or is likely to dazzle or distract a person providing air traffic services.
The offense is a strict liability offense, meaning that prosecutors do not need to prove that the person shining the laser intended to endanger the vehicle or air traffic facility/controller. There are two defenses allowed: 1) the person had a reasonable excuse for shining the laser beam, or 2) the person did not intend to shine a laser at the vehicle/ATF/controller and exercised all due diligence to avoid doing so.
Click to read more...
The penalties for violations are up to five years imprisonment and an unlimited fine; these penalties take effect starting July 10 2018.
The law applies to laser beams aimed at aircraft, motor vehicles, trains, ships, hovercraft and other vehicles. A vehicle does not have to be moving at the time of offense; if the engine or motor is running then the law applies. Another provision makes it an offense to shine or direct a laser beam towards an air traffic facility, or a person providing air traffic services, under the condition where the beam dazzles or distracts, or is likely to dazzle or distract a person providing air traffic services.
The offense is a strict liability offense, meaning that prosecutors do not need to prove that the person shining the laser intended to endanger the vehicle or air traffic facility/controller. There are two defenses allowed: 1) the person had a reasonable excuse for shining the laser beam, or 2) the person did not intend to shine a laser at the vehicle/ATF/controller and exercised all due diligence to avoid doing so.
Click to read more...
Canada: Looking at "all possible options" to fight laser incidents; perhaps a ban and mandatory labels
18 Feb 2018 -- Categories: Laws | Bans & Restrictions | Easy availability | Statistics | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
Minister Marc Garneau announced February 15 2018 that Transport Canada will explore “all possible options” to reduce the number of laser pointer/aircraft incidents, and will announce measures “in the coming weeks.”
The statement came after six laser incidents over two days earlier in the month, at Montreal’s Trudeau Airport. Garneau said these made him “very, very mad.”
A Transport official said the options include a ban on importation of powerful lasers, mandatory warning labels, and stronger penalties for those who are caught.
Garneau noted that it is hard to catch a laser perpetrator, making prosecutions “few and far between”. He believes that some people are not aware of the bright-light danger of laser light, but that others “know darn well what they’re doing” and are trying to “provoke something.”
Transport Canada currently has a program called “Not-a-Bright-Idea,” trying to educate the general public about the risks and legal consequences of aiming lasers at aircraft. Since implementing the program in May 2016, laser incident numbers have dropped. There were 590 reported incidents in 2015, 527 in 2016, and 379 in 2017.
Garneau said that despite the 28 percent drop, Transport Canada must do more, and that is why they are exploring other options.
From 660 News and AVweb
Note: In response to a LaserPointerSafety.com request, an email address for interested persons was provided: “Transport Canada is exploring options to reduce laser strikes. Canadians and industry members can provide information to the Civil Aviation Communications Centre by emailing: services@tc.gc.ca”
The statement came after six laser incidents over two days earlier in the month, at Montreal’s Trudeau Airport. Garneau said these made him “very, very mad.”
A Transport official said the options include a ban on importation of powerful lasers, mandatory warning labels, and stronger penalties for those who are caught.
Garneau noted that it is hard to catch a laser perpetrator, making prosecutions “few and far between”. He believes that some people are not aware of the bright-light danger of laser light, but that others “know darn well what they’re doing” and are trying to “provoke something.”
Transport Canada currently has a program called “Not-a-Bright-Idea,” trying to educate the general public about the risks and legal consequences of aiming lasers at aircraft. Since implementing the program in May 2016, laser incident numbers have dropped. There were 590 reported incidents in 2015, 527 in 2016, and 379 in 2017.
Garneau said that despite the 28 percent drop, Transport Canada must do more, and that is why they are exploring other options.
From 660 News and AVweb
Note: In response to a LaserPointerSafety.com request, an email address for interested persons was provided: “Transport Canada is exploring options to reduce laser strikes. Canadians and industry members can provide information to the Civil Aviation Communications Centre by emailing: services@tc.gc.ca”
UK: New UK law to provide stronger penalties, easier prosecution for aiming a laser at a vehicle
The following press release is from the U.K. Department of Transport, published December 20 2017. The Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Bill is a pending law so as of this date, it is not in force. (UPDATED January 8 2018 - The bill will be read on January 9 2018 in the House of Lords. Thanks to John O’Hagan for this update.) (UPDATED May 10 2018 - The bill gained Royal Assent so now is a law, the Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Act. The act’s penalties take effect starting July 10 2018)
The text of the bill is here. A House of Lords Summary Briefing, giving some background, is here.
Tough new penalties for misuse of lasers
People who target transport operators with laser devices could be jailed for up to 5 years under new laws designed to protect the public.
The Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Bill, which was published today (20 December 2017), will also expand the list of vehicles, beyond just planes, which it is an offence to target with lasers.
Drivers of trains and buses, captains of boats and even pilots of hovercraft will be among those protected by the new legislation.
The bill will make it easier to prosecute offenders by removing the need to prove an intention to endanger a vehicle.
And it will remove the cap on the amount offenders can be fined – which is currently limited to £2,500 – paving the way for substantial sanctions. Fines could be issued in isolation or alongside a prison sentence.
The police will also be given additional powers to catch those responsible for the misuse of lasers.
Aviation Minister, Baroness Sugg said:
“Lasers can dazzle, distract or blind those in control of a vehicle, with serious and potentially even fatal consequences.”
“The government is determined to protect pilots, captains, drivers and their passengers and take action against those who threaten their safety.”
Alongside their existing powers of arrest and the ability to search a person once arrested, officers will no longer need to establish proof of intention endanger to a vehicle, aircraft or vessel, making it easier to prosecute swiftly. It will be an offence to shine or direct a laser towards a vehicle if it dazzles or distracts the operator, if done deliberately or if reasonable precautions to avoid doing so are not taken.Click to read more...
The text of the bill is here. A House of Lords Summary Briefing, giving some background, is here.
Tough new penalties for misuse of lasers
People who target transport operators with laser devices could be jailed for up to 5 years under new laws designed to protect the public.
The Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Bill, which was published today (20 December 2017), will also expand the list of vehicles, beyond just planes, which it is an offence to target with lasers.
Drivers of trains and buses, captains of boats and even pilots of hovercraft will be among those protected by the new legislation.
The bill will make it easier to prosecute offenders by removing the need to prove an intention to endanger a vehicle.
And it will remove the cap on the amount offenders can be fined – which is currently limited to £2,500 – paving the way for substantial sanctions. Fines could be issued in isolation or alongside a prison sentence.
The police will also be given additional powers to catch those responsible for the misuse of lasers.
Aviation Minister, Baroness Sugg said:
“Lasers can dazzle, distract or blind those in control of a vehicle, with serious and potentially even fatal consequences.”
“The government is determined to protect pilots, captains, drivers and their passengers and take action against those who threaten their safety.”
Alongside their existing powers of arrest and the ability to search a person once arrested, officers will no longer need to establish proof of intention endanger to a vehicle, aircraft or vessel, making it easier to prosecute swiftly. It will be an offence to shine or direct a laser towards a vehicle if it dazzles or distracts the operator, if done deliberately or if reasonable precautions to avoid doing so are not taken.Click to read more...
US: 134 laser arrests, 80 convictions, out of 17,725 incidents, 2005-2013
21 May 2014 -- Categories: Statistics | Fines & Jail | Arrests | Finding perpetrators | Laws | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
According to Ars Technica writer Cyrus Farivar, in the U.S. from 2005 to 2013 there were 134 arrests for aiming lasers at aircraft, out of 17,725 FAA-reported lasing incidents. He wrote “That means that even amongst reported incidents, there’s only a 0.75 percent chance of getting caught. Adding countless unreported incidents would only make that minuscule percentage go down further.”
Farivar noted that there were 80 convictions among the 134 arrests. One reason for the conviction rate of 60%: some who were arrested were minors who were never formally charged.
The extensively researched 4,200-word article, dated May 21 2014, was based around the 14-year sentence handed down in March 2014 to Sergio Rodriguez, for his August 2012 aiming of a laser at two helicopters, one medical and one police. Farivar used the case to illustrate many laser/aviation issues, especially about how prosecution is being used to try to educate and deter future incidents.
Farivar interviewed Karen Escobar, who has brought more cases against laser perpetrators than any other federal prosecutor. Her territory includes Sacramento, Fresno, and Bakersfield.
In the article, Escobar was quoted as saying “At sentencing, [Rodriguez] did not accept responsibility for his actions; he blamed his 2- and 3- year-old children. I believe the evidence showed the laser was a dangerous weapon, and there was intention, supporting a guideline sentence of 168 months. I would not call it harsh. I would say it is a penalty that fits the crime, but I believe that it will have a deterrent effect, and I hope it will.”
Farivar noted that, “While 14 years might sound incredibly excessive for an incident that caused no serious or lasting physical injury, much less death, this is the emerging reality for attorneys prosecuting laser strikes. The Rodriguez sentence now serves as an example of what can happen to defendants who don't take plea deals. (The plea deals typically end up being around two years.)”
From Ars Technica
Farivar noted that there were 80 convictions among the 134 arrests. One reason for the conviction rate of 60%: some who were arrested were minors who were never formally charged.
The extensively researched 4,200-word article, dated May 21 2014, was based around the 14-year sentence handed down in March 2014 to Sergio Rodriguez, for his August 2012 aiming of a laser at two helicopters, one medical and one police. Farivar used the case to illustrate many laser/aviation issues, especially about how prosecution is being used to try to educate and deter future incidents.
Farivar interviewed Karen Escobar, who has brought more cases against laser perpetrators than any other federal prosecutor. Her territory includes Sacramento, Fresno, and Bakersfield.
In the article, Escobar was quoted as saying “At sentencing, [Rodriguez] did not accept responsibility for his actions; he blamed his 2- and 3- year-old children. I believe the evidence showed the laser was a dangerous weapon, and there was intention, supporting a guideline sentence of 168 months. I would not call it harsh. I would say it is a penalty that fits the crime, but I believe that it will have a deterrent effect, and I hope it will.”
Farivar noted that, “While 14 years might sound incredibly excessive for an incident that caused no serious or lasting physical injury, much less death, this is the emerging reality for attorneys prosecuting laser strikes. The Rodriguez sentence now serves as an example of what can happen to defendants who don't take plea deals. (The plea deals typically end up being around two years.)”
From Ars Technica
US: UPDATED - Arizona bill to make aiming a laser at aircraft a felony
06 Jan 2014 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Laws | Ways to reduce incidents | Eye effect or injury | Updated story | SLA news
A bill will be introduced January 13 2014 by Arizona Representative Ethan Orr, making it a felony to point a laser at an aircraft. It would apply to all aircraft, including passenger planes and helicopters.
The Tucson Police Department had about 50 lasing incidents in 2013; the perpetrator was caught in most of the cases. But there was little prosecution.
Orr says the bill is needed because “there’s really no punishment. The county prosecutor, because it's not at a felony status, doesn't go after them. And so literally, you get a ticket and nothing happens. But you're endangering lives."
Orr is working with Tucson police pilot Chris Potter, who says he has been hit by a laser pointer about 100 times in his career. Potter says a laser pointer permanently damaged his right eye around 2011.
According to News 4 Tucson, “the FBI will launch a public awareness campaign about the issue next month.” It was not clear if this was an Arizona-area initiative or nationwide.
From News 4 Tucson
UPDATED - February 4 2014: The Arizona House Judiciary Committee voted in favor of increasing the penalty for persons who point lasers at aircraft. HB 2164 would make it a Class 5 felony, with a presumptive sentence of 18 months in prison, to knowingly or intentionally point a laser at an occupied aircraft. And the penalty would go to 30 months if the act disables the pilot or causes serious physical injury to anyone on board. The legislator who introduced the bill, Ethan Orr, is considering reducing the penalty slightly, to a Class 6 felony, when it goes to the full House. Prosecutors could reduce the charge from a felony to a misdemeanor when appropriate. Orr said this might be the case for youths so that a single mistake would not result in a felony record. From KWST.com. A related article at AZCentral.com includes comments from LaserPointerSafety.com’s Patrick Murphy on the issue.
UPDATE 2 - May 1 2014: The bill was eventually amended to make the act of aiming at an aircraft a Class 1 misdemeanor. The act became an assault if the pilot was unable to safely operate the aircraft or if anyone onboard suffered a serious physical injury. The amended version passed both legislative bodies and was sent to Governor Jan Brewer, who signed it on April 30 2014. From the Arizona State Legislature legislative history of HB2164.
UPDATE 3 - September 23 2014: The Arizona Police Association and other law enforcement groups want to increase the penalty to a felony. They hope to introduce a measure when the legislature re-convenes in January 2015.
The Tucson Police Department had about 50 lasing incidents in 2013; the perpetrator was caught in most of the cases. But there was little prosecution.
Orr says the bill is needed because “there’s really no punishment. The county prosecutor, because it's not at a felony status, doesn't go after them. And so literally, you get a ticket and nothing happens. But you're endangering lives."
Orr is working with Tucson police pilot Chris Potter, who says he has been hit by a laser pointer about 100 times in his career. Potter says a laser pointer permanently damaged his right eye around 2011.
According to News 4 Tucson, “the FBI will launch a public awareness campaign about the issue next month.” It was not clear if this was an Arizona-area initiative or nationwide.
From News 4 Tucson
UPDATED - February 4 2014: The Arizona House Judiciary Committee voted in favor of increasing the penalty for persons who point lasers at aircraft. HB 2164 would make it a Class 5 felony, with a presumptive sentence of 18 months in prison, to knowingly or intentionally point a laser at an occupied aircraft. And the penalty would go to 30 months if the act disables the pilot or causes serious physical injury to anyone on board. The legislator who introduced the bill, Ethan Orr, is considering reducing the penalty slightly, to a Class 6 felony, when it goes to the full House. Prosecutors could reduce the charge from a felony to a misdemeanor when appropriate. Orr said this might be the case for youths so that a single mistake would not result in a felony record. From KWST.com. A related article at AZCentral.com includes comments from LaserPointerSafety.com’s Patrick Murphy on the issue.
UPDATE 2 - May 1 2014: The bill was eventually amended to make the act of aiming at an aircraft a Class 1 misdemeanor. The act became an assault if the pilot was unable to safely operate the aircraft or if anyone onboard suffered a serious physical injury. The amended version passed both legislative bodies and was sent to Governor Jan Brewer, who signed it on April 30 2014. From the Arizona State Legislature legislative history of HB2164.
UPDATE 3 - September 23 2014: The Arizona Police Association and other law enforcement groups want to increase the penalty to a felony. They hope to introduce a measure when the legislature re-convenes in January 2015.
US: Newsday editorial calls for warnings, enforcements to reduce laser attacks
The Long Island-based newspaper Newsday, in an editorial published August 23 2012, called for additional warnings and prosecutions to help reduce incidents of pointing lasers at aircraft.
The paper, ranked 13th in the country with a circulation of 393,000 weekday subscribers, said “It’s a serious offense that should be firmly punished…. Heavy fines, and in some cases, jail time, would send a powerful message that it’s a life-threatening crime.”
The editorial was the result of incidents in the Long Island area in the past month. It was titled “Enforce anti-laser laws with laser-like force.”
From Newsday. Subscriber information from USA Today.
The paper, ranked 13th in the country with a circulation of 393,000 weekday subscribers, said “It’s a serious offense that should be firmly punished…. Heavy fines, and in some cases, jail time, would send a powerful message that it’s a life-threatening crime.”
The editorial was the result of incidents in the Long Island area in the past month. It was titled “Enforce anti-laser laws with laser-like force.”
From Newsday. Subscriber information from USA Today.
UK: Pilots want jail for persons aiming laser pens at aircraft
26 Jun 2013 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Laws | Bans & Restrictions | Finding perpetrators | Fines & Jail | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
The British Airline Pilots’ Association warned about the hazards of laser pens directed at aircraft, and called for prison sentences for the perpetrators. They noted that there were more than 1,500 incidents in 2012, with “only a handful of those responsible” being prosecuted.
BALPA general secretary Jim McAuslan asked for a government cross-agency summit to address the problem. BALPA requested stronger regulations restricting the sale of high-powered lasers, more prosecutions, and action taken through trading standards.
He said that hotspots include airports at Manchester, Glasgow, Liverpool and Heathrow.
From ITV London and ITV Granada
BALPA general secretary Jim McAuslan asked for a government cross-agency summit to address the problem. BALPA requested stronger regulations restricting the sale of high-powered lasers, more prosecutions, and action taken through trading standards.
He said that hotspots include airports at Manchester, Glasgow, Liverpool and Heathrow.
From ITV London and ITV Granada
Scotland: Pilots want stepped-up prosecution against laser attacks
08 Apr 2013 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Laws | Arrests | Finding perpetrators | Statistics | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
“Prosecution rates for laser attacks need to improve,” according to a spokesperson for the British Airline Pilots’ Association (BALPA). “We need the judiciary to get on top of the problem …. small fines or warnings for perpetrators of these attacks is not enough; anyone shining a laser at an aircraft recklessly should receive an automatic prison sentence.”
An April 2013 investigation by the Scottish Express found 338 incidents in Scotland from January 1 2011 through February 13 2013. Only 12, or 3.5 percent, had been solved. The paper noted that the International Air Transport Authority (IATA) suggests there are 12 incidents involving lasers each day globally. [Note: The U.S. rate is approximately 9-10 per day, indicating the rest of the world’s rate is 2-3 per day which LaserPointerSafety.com believes to be higher.] An IATA spokesperson said the organization “support[s] strong penalties for anyone caught engaging in the act.”
The U.K.’s Civil Aviation Authority said there were 152 laser incidents at Heathrow Airport in 2012, compared with 136 incidents at Glascow Airport which has 1/10 the number of passengers.
The Scottish Express story contains additional statistics on Scotland airport lasing rates.
From the Scottish Express
An April 2013 investigation by the Scottish Express found 338 incidents in Scotland from January 1 2011 through February 13 2013. Only 12, or 3.5 percent, had been solved. The paper noted that the International Air Transport Authority (IATA) suggests there are 12 incidents involving lasers each day globally. [Note: The U.S. rate is approximately 9-10 per day, indicating the rest of the world’s rate is 2-3 per day which LaserPointerSafety.com believes to be higher.] An IATA spokesperson said the organization “support[s] strong penalties for anyone caught engaging in the act.”
The U.K.’s Civil Aviation Authority said there were 152 laser incidents at Heathrow Airport in 2012, compared with 136 incidents at Glascow Airport which has 1/10 the number of passengers.
The Scottish Express story contains additional statistics on Scotland airport lasing rates.
From the Scottish Express
US: First comments on new U.S. law, from Western Pa. prosecutor
On February 14 2012, President Obama signed a law making it illegal to aim a laser pointer at an aircraft, or its flight path. The first official comment we have seen on this law comes from David Hickton, U.S. Attorney for Western Pennsylvania. He was quoted on February 27 as saying “This is a serious federal crime which could cause disastrous consequences and will have serious repercussions in the criminal justice system.”
Hickton noted that the new law makes it easier to prosecute since malicious intent is no longer required. Instead, it must be proven that the defendant “knowingly” targeted an aircraft or its flight path with a laser pointer. The new law’s penalty is up to $250,000 fine and/or prison for up to five years.
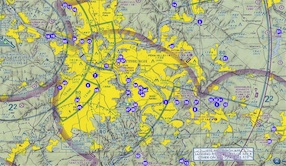
A map from the FAA Allegheny Flight Standards District Office shows the location of 51 laser events between September 2009 and October 2011. Arrests were made in only two of these cases: “Hickton and other officials concede it can be difficult to pinpoint culprits.”
Hickton noted that the new law makes it easier to prosecute since malicious intent is no longer required. Instead, it must be proven that the defendant “knowingly” targeted an aircraft or its flight path with a laser pointer. The new law’s penalty is up to $250,000 fine and/or prison for up to five years.
A map from the FAA Allegheny Flight Standards District Office shows the location of 51 laser events between September 2009 and October 2011. Arrests were made in only two of these cases: “Hickton and other officials concede it can be difficult to pinpoint culprits.”
From 90.5 FM Essential Public Radio and the Pittsburgh Tribune-Review. A press release from Hickton’s office is below (click the Read More link). Edited Feb. 28 2012 at 3:15 PM EST to correct a statement from 90.5 FM.
Canada: Man gets lower fine, in part because pilot did not lose control
In a case which may have Canadian implications for laser users’ defense, a judge reduced the fine for an Edmonton man charged with creating a hazard to aviation safety.
Provincial Judge Paul Sully said the August 19 2009 incident was "not as serious” as the prosecutor described, since the pilot did not lose control, but instead was "momentarily blinded from viewing his instruments [and] was able to complete his orbits.” In addition, the judge noted that the pilot was familiar with the dangers of laser light.
Judge Sully also rejected the prosecution’s notion that the man should have culpability: “The offender had a momentary loss of common sense which resulted from his failure to recognize the high standard of care needed when handling a laser.”Click to read more...
Provincial Judge Paul Sully said the August 19 2009 incident was "not as serious” as the prosecutor described, since the pilot did not lose control, but instead was "momentarily blinded from viewing his instruments [and] was able to complete his orbits.” In addition, the judge noted that the pilot was familiar with the dangers of laser light.
Judge Sully also rejected the prosecution’s notion that the man should have culpability: “The offender had a momentary loss of common sense which resulted from his failure to recognize the high standard of care needed when handling a laser.”Click to read more...