Home
A comprehensive resource for safe and responsible laser use
Poland: Scientific paper says laser toy is misclassified, 4x legally required power
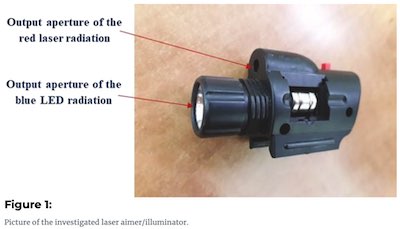
The paper examined the red laser's output and found it was 1.7 milliwatts. This is four times the Class 1 limit of <0.39 mW, and is 1.7 times the Class 2 limit of <1 mW. The laser should have been classified as Class 3R (<5 mW limit).
The author notes that according to the European standard EN 62115:2020, and guidance from Public Health England, laser toys should be Class 1. At four times the Class 1 limit, this toy's "radiation may be hazardous, especially when looking into the beam for long periods."
From Mlynczak, Jaroslaw. "Laser toys fail to comply with safety standards – case study based on laser product classification" Advanced Optical Technologies , no. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/aot-2020-0072
COMMENTARY FROM LASERPOINTERSAFETY.COM
We do not dispute Mlynczak's technical findings. However, there are some misleading or false statements in the paper that we would like to address.
- An erroneous title; it should be "Laser toy fails to comply…" The case study is not about "toys" plural. It covers only one sample of one toy rifle which had a laser aiming device that was found to be misclassified.
- Stating that the toy laser's output power (1.7 mW) is illegal, when it may have been legal or close to legal (within 0.7 mW) at time of sale.
- Calling the laser's light output "radiation" 14 times and never using the more precise term "light," thus giving a misleading impression the hazard might be similar to that of X-radiation or nuclear radiation.
- Stating without any proof or reference that children "will usually try to look directly into the laser beam."
- Stating without any proof or reference that children "could have temporary disturbances of vision… lead[ing] to a tragedy."
- Stating without any proof or reference that there is such a thing as "hypersensitivity to laser radiation."
- Stating without any proof or reference that "the described laser toy… [is] easily available and [is] still sold as toys in many European states."
- Listing in the References studies claiming laser "toy" injuries, which actually were from standard, non-toy laser pointers.
Details are below:Click to read more...
US: High-powered lasers can be obtained from inside a Christmas holiday laser projector
In a January 22 2018 Hackaday post, Tom Nardi purchased a “Home Accents Holiday Multi-Color Light Projector” from a hardware chain on clearance, marked down from $56 to just $14.
He removed the cover with four screws and found the parts inside used connectors instead of solder: “It’s like they wanted us to strip it for parts.”
The lasers were defocused inside. “…[A]t 3 meters the spots looked as large as dinner plates…. Once focused, it becomes pretty clear that these lasers are quite a bit more powerful than the <5 mW listed on the product’s warning sticker.”
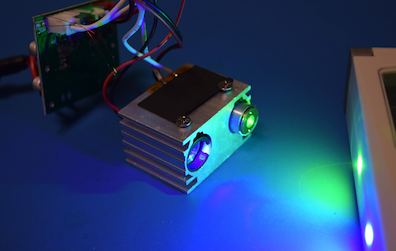
The green and blue laser diode modules inside the holiday projector
Nardi noted that the blue laser, when focused, was “easily able to burn pieces of paper and punch holes in black plastic.” He also estimated that the green laser was “at least twice as bright” as a laser pointer he owns that claims to be 50 mW: “…it certainly would not surprise me if they are both [green and blue] at least 100 mW.”
Nardi writes: “If your biggest take-away from this post is that the Home Depot is selling a 440 nm laser you can use to burn stuff, I certainly don’t blame you.”
From Hackaday. LaserPointerSafety.com has a page with more information, including measurements of the beam output of a Star Shower projector, here.
Commentary from LaserPointerSafety.com: In fairness to Home Accents, the FDA-required warning sticker has to do with the laser power of the unopened unit in its factory configuration. Class 3R (IIIa) laser projectors like this are not allowed in the U.S. to be over 5 mW output power. It may be that after going through the holographic diffraction grating that creates the stars, that the Home Accents projector meets Food and Drug Administration requirements for user access to laser light.
US: FDA proposes defacto ban on selling pointers, handhelds above 5 milliwatts
Although the agency did not give a reason, such bans have been imposed in other countries in response to climbing numbers of laser illuminations of aircraft as well as reports of eye injuries caused by higher-powered consumer lasers.
The proposal would not make it illegal to own or responsibly use portable, battery-powered lasers of 5 mW or more. However, manufacturers could not make or sell these into general commerce in the U.S.
The agency will accept comments for 90 days (until August 2 2014) on the new proposal. FDA will then review the comments. Based on whether it believes any objections or suggestions are valid, the agency could put the guidance into effect (thus imposing their new interpretation), could submit a revised proposal, or could withdraw its proposal.
What lasers are covered by the proposed 5 mW limit?
FDA does not have direct authority over battery powered portable lasers. For example, the words “pointer” and “handheld” laser do not appear in U.S. laser regulations 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11.
Therefore, to regulate these lasers, the May 5 draft proposes an extension of the FDA’s existing authority to regulate surveying, leveling and alignment (“SLA”) lasers. In the May 5 proposal, FDA asserts that the existing definition of SLA lasers also can applied to lasers with the following design characteristics:
- Compact size (i.e. small, lightweight)
- Battery power
- Ergonomic design to permit hand-held use
- An aperture in the laser product's protective housing to transmit laser emission into open space
- Portability to permit use in open spaces or in unrestricted environments
- Features that utilize the laser’s straight line emission for surveying, leveling, or alignment
According to the FDA, these types of lasers would be affected by the new 5 mW limit:
- Laser pointers
- Levels
- Tools incorporating laser guides
- Gun sights
- Target designators
- Night vision illuminators
- Visual disruptors
What lasers are NOT covered by the proposed 5 mW limit?
The FDA's proposed 5 mW limit would NOT apply to lasers with the following design characteristics:
- Predictable, stable power input and output
- High quality power supply and/or power conditioning components
- Adjustability of power and wavelength
- Design that facilitates remote actuation
- Non-portability
- Hard wire connection to power mains
From the FDA’s Surveying, Leveling, or Alignment Laser Products - Draft Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff webpage, published online May 2 2014. This webpage includes the procedure for submitting comments to FDA.The FDA’s PDF version of the draft guidance document is here.
Editorial comment from LaserPointerSafety.com: We have previously published our opinion disagreeing with the FDA’s interpretation of “SLA” lasers. The existing regulations are clear on what constitutes “surveying, leveling or alignment” (SLA) lasers. While we understand the FDA’s intent, in our view, they are going about it the wrong way. They are essentially “making it up” by adding characteristics (size, battery power) which are in no way derived from the clear, existing definition of SLA lasers. As support of this position, we have not found any surveying, leveling or alignment lasers which look the same as the majority of laser pointers and handhelds. This topic is discussed in much greater detail on our page describing FDA authority over laser pointers and handheld lasers.