Home
A comprehensive resource for safe and responsible laser use
US: GAO report has three recommendations for FAA
On August 18 2022 the U.S. General Accounting Office (GAO) issued a report prepared for Congress. The title is "Aviation Safety: FAA Should Strengthen Efforts to Address the Illegal Practice of Intentionally Aiming Lasers at Aircraft."
The GAO began their study of the issue in November 2020. Their goal was to determine:
• "the extent to which [the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration] FAA and other federal agencies take enforcement action against those who point lasers at aircraft and challenges with investigations and reporting;"
• "public outreach efforts FAA and other federal agencies have taken to deter laser incidents, and what actions, if any, would strengthen these efforts; and"
• "options that stakeholders have identified to mitigate the effects of laser incidents, and the potential benefits and challenges to implementation."
FINDINGS
The following is from the "What GAO Found" summary of their findings:
"Aiming a laser at an aircraft can distract or disorient pilots and is a federal crime. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) investigates laser incidents, pursues civil penalties, and assists the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and U.S. Attorneys with investigations. Given the nature of laser incidents, FAA and federal law enforcement face difficulties identifying those involved. However, they have taken some enforcement actions, resulting in penalties ranging from $50 to $27,388 and sentences of up to 51 months, according to GAO analysis."
"To support incident investigations, FAA asks that pilots complete an incident questionnaire upon landing. However, FAA received responses for about 12 percent of the 8,221 laser incidents that occurred over a recent one-year period from 2020 to 2021. Reasons identified by FAA and others for the low response rate include the length of the questionnaire and its voluntary nature. Further, FAA does not consistently share collected information with law enforcement."
"In 2016, Congress required FAA to report quarterly on laser incidents, including data on civil and criminal actions. However, GAO found FAA’s reports to be incomplete. For example, GAO’s analysis shows 44 prosecutions from July 2016 through September 2020, when FAA reported only four. FAA officials said they do not routinely request data on the status of actions from other agencies and face challenges, such as access to this data. By not routinely seeking updates from agencies, FAA does not provide Congress with a complete picture of laser incident investigations and enforcement actions as required."
"FAA, FBI, and the Food and Drug Administration, which has regulatory authority over lasers, each conduct outreach to educate the public about laser incidents. These agencies were involved in an interagency group to address laser safety concerns until 2015 when the group dissolved. Since then, laser incidents have increased and identifying subjects remains difficult. FAA is well positioned to lead an interagency effort to explore re-establishing this group, given FAA’s responsibility for the safety of the national airspace."
RECOMMENDATIONS
The 46-page report recommended three actions to be taken by FAA:
1: "The FAA Administrator should determine what information from pilots and crewmembers would be most useful for investigating laser incidents, and how best to collect the information and to share it with law enforcement."
2: "The FAA Administrator should improve its quarterly reports to Congress on laser incidents by routinely seeking information from other agencies on related federal investigation and enforcement actions and disclosing, in those reports, any limitations with the data."
3: "The FAA Administrator should work with FBI and FDA to explore re-establishing an interagency working group on outreach to educate the public on the hazards of lasers and the illegality of aiming lasers at aircraft."
From the GAO webpage about the report. It includes a link to the full 46-page report.
COMMENTARY FROM LASERPOINTERSAFETY.COM
While the three recommendations are useful, we are disappointed that the GAO report did not make a primary recommendation that FAA should require pilot training on how to handle laser illuminations. In our view, this is the single most important safety step that FAA could take.
The report does discuss this, beginning on page 30 with this paragraph:
"Most stakeholders told us that training pilots on how to respond to laser incidents is an important mitigation strategy. For example, representatives from an organization representing law enforcement pilots told us that training pilots in responding to laser incidents is important because there will always be laser incidents. These representatives said that even with effective public outreach and enforcement activities, there would be people intentionally trying to harm aircraft and that in these situations, it is important for pilots to know how to react. Additionally, representatives from a group representing pilots told us they recommend airlines develop and incorporate a laser strike training module at a minimum of every 2 years." (emphasis added)
However, the GAO report simply lists some pilot training efforts. It does not say that FAA should mandate this.
LaserPointerSafety.com has also recommended that pilots be exposed to safe, simulated laser light during simulator training. This gives a flavor of what a bright light disruption can be and helps "inoculate" pilots so they know what to do, just as they train for other aviation emergencies.
The GAO began their study of the issue in November 2020. Their goal was to determine:
• "the extent to which [the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration] FAA and other federal agencies take enforcement action against those who point lasers at aircraft and challenges with investigations and reporting;"
• "public outreach efforts FAA and other federal agencies have taken to deter laser incidents, and what actions, if any, would strengthen these efforts; and"
• "options that stakeholders have identified to mitigate the effects of laser incidents, and the potential benefits and challenges to implementation."
FINDINGS
The following is from the "What GAO Found" summary of their findings:
"Aiming a laser at an aircraft can distract or disorient pilots and is a federal crime. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) investigates laser incidents, pursues civil penalties, and assists the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and U.S. Attorneys with investigations. Given the nature of laser incidents, FAA and federal law enforcement face difficulties identifying those involved. However, they have taken some enforcement actions, resulting in penalties ranging from $50 to $27,388 and sentences of up to 51 months, according to GAO analysis."
"To support incident investigations, FAA asks that pilots complete an incident questionnaire upon landing. However, FAA received responses for about 12 percent of the 8,221 laser incidents that occurred over a recent one-year period from 2020 to 2021. Reasons identified by FAA and others for the low response rate include the length of the questionnaire and its voluntary nature. Further, FAA does not consistently share collected information with law enforcement."
"In 2016, Congress required FAA to report quarterly on laser incidents, including data on civil and criminal actions. However, GAO found FAA’s reports to be incomplete. For example, GAO’s analysis shows 44 prosecutions from July 2016 through September 2020, when FAA reported only four. FAA officials said they do not routinely request data on the status of actions from other agencies and face challenges, such as access to this data. By not routinely seeking updates from agencies, FAA does not provide Congress with a complete picture of laser incident investigations and enforcement actions as required."
"FAA, FBI, and the Food and Drug Administration, which has regulatory authority over lasers, each conduct outreach to educate the public about laser incidents. These agencies were involved in an interagency group to address laser safety concerns until 2015 when the group dissolved. Since then, laser incidents have increased and identifying subjects remains difficult. FAA is well positioned to lead an interagency effort to explore re-establishing this group, given FAA’s responsibility for the safety of the national airspace."
RECOMMENDATIONS
The 46-page report recommended three actions to be taken by FAA:
1: "The FAA Administrator should determine what information from pilots and crewmembers would be most useful for investigating laser incidents, and how best to collect the information and to share it with law enforcement."
2: "The FAA Administrator should improve its quarterly reports to Congress on laser incidents by routinely seeking information from other agencies on related federal investigation and enforcement actions and disclosing, in those reports, any limitations with the data."
3: "The FAA Administrator should work with FBI and FDA to explore re-establishing an interagency working group on outreach to educate the public on the hazards of lasers and the illegality of aiming lasers at aircraft."
From the GAO webpage about the report. It includes a link to the full 46-page report.
COMMENTARY FROM LASERPOINTERSAFETY.COM
While the three recommendations are useful, we are disappointed that the GAO report did not make a primary recommendation that FAA should require pilot training on how to handle laser illuminations. In our view, this is the single most important safety step that FAA could take.
The report does discuss this, beginning on page 30 with this paragraph:
"Most stakeholders told us that training pilots on how to respond to laser incidents is an important mitigation strategy. For example, representatives from an organization representing law enforcement pilots told us that training pilots in responding to laser incidents is important because there will always be laser incidents. These representatives said that even with effective public outreach and enforcement activities, there would be people intentionally trying to harm aircraft and that in these situations, it is important for pilots to know how to react. Additionally, representatives from a group representing pilots told us they recommend airlines develop and incorporate a laser strike training module at a minimum of every 2 years." (emphasis added)
However, the GAO report simply lists some pilot training efforts. It does not say that FAA should mandate this.
LaserPointerSafety.com has also recommended that pilots be exposed to safe, simulated laser light during simulator training. This gives a flavor of what a bright light disruption can be and helps "inoculate" pilots so they know what to do, just as they train for other aviation emergencies.
US: FAA credits "heightened public awareness" for lowering laser incident numbers in 2017 and 2018
An April 11 2019 news item from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration says that "Heightened public awareness of the serious safety risk posed by lasers reduced the total number of laser strikes for the second consecutive year…."
Incidents reported to FAA have declined from 7,398 reports in 2016, to 6,754 reports in 2017, and 5,663 reports in 2018, the last full year for which statistics are available.
According to FAA, "the agency and law enforcement agencies are working hard to increase public awareness of the dangers posed by lasers."
The news item linked to a page entitled "Laser Incidents and Legal Interpretation of the Law", a new video published April 10 2019 on YouTube, entitled "Laser Strikes on Aircraft Pilots", and an April 10 2019 Fact Sheet on lasers.
One paragraph of the fact sheet says that "The FAA’s guidance for agency investigators and attorneys stresses that laser violations should not be addressed through warning notices or counseling. The agency seeks moderately high civil penalties for inadvertent violations, but maximum penalties for deliberate violations. Violators who are pilots or mechanics face revocation of their FAA certificate, as well as civil penalties."
From FAA news item "Outreach Helps Bring Laser Strike Numbers Down"
COMMENTARY FROM LASERPOINTERSAFETY.COM:
We are not aware of any recent (2015-2018) campaign by FAA to increase public awareness.
In 2014, there was a publicity campaign by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) in 12 U.S. cities between February 11 and April 11 2014, which offered a $10,000 reward for information about anyone pointing a laser at an aircraft. This was expanded nationwide between June 3 and September 1 2014. During 2014 there was a 12.8% decline in laser incidents compared to 2013. It is not known how much the FBI publicity campaign contributed to the decline.
In our view, there may be other reasons for the decline. For example, pilots may be tiring of reporting laser illuminations with no apparent follow-up or effect. This would lead to a decline in reported incidents.
We are not aware of any studies done to determine the reasons for declines in reported laser incidents.
To summarize, it seems incorrect to attribute the lower number of laser incidents to "heightened public awareness." In fact, there is some anecdotal evidence that publicity actually leads to copycat laser incidents.
Incidents reported to FAA have declined from 7,398 reports in 2016, to 6,754 reports in 2017, and 5,663 reports in 2018, the last full year for which statistics are available.
According to FAA, "the agency and law enforcement agencies are working hard to increase public awareness of the dangers posed by lasers."
The news item linked to a page entitled "Laser Incidents and Legal Interpretation of the Law", a new video published April 10 2019 on YouTube, entitled "Laser Strikes on Aircraft Pilots", and an April 10 2019 Fact Sheet on lasers.
One paragraph of the fact sheet says that "The FAA’s guidance for agency investigators and attorneys stresses that laser violations should not be addressed through warning notices or counseling. The agency seeks moderately high civil penalties for inadvertent violations, but maximum penalties for deliberate violations. Violators who are pilots or mechanics face revocation of their FAA certificate, as well as civil penalties."
From FAA news item "Outreach Helps Bring Laser Strike Numbers Down"
COMMENTARY FROM LASERPOINTERSAFETY.COM:
We are not aware of any recent (2015-2018) campaign by FAA to increase public awareness.
In 2014, there was a publicity campaign by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) in 12 U.S. cities between February 11 and April 11 2014, which offered a $10,000 reward for information about anyone pointing a laser at an aircraft. This was expanded nationwide between June 3 and September 1 2014. During 2014 there was a 12.8% decline in laser incidents compared to 2013. It is not known how much the FBI publicity campaign contributed to the decline.
In our view, there may be other reasons for the decline. For example, pilots may be tiring of reporting laser illuminations with no apparent follow-up or effect. This would lead to a decline in reported incidents.
We are not aware of any studies done to determine the reasons for declines in reported laser incidents.
To summarize, it seems incorrect to attribute the lower number of laser incidents to "heightened public awareness." In fact, there is some anecdotal evidence that publicity actually leads to copycat laser incidents.
US: Utah National Guard reluctant to report laser cases to FBI, apparently after suspect's suicide
Utah National Guard pilots have not reported incidents where lasers were aimed at their aircraft since at least September 2009, according to an August 30 2017 news story in the South Valley (Utah) Journal.
In an interview, Chief Warrant Officer Robert Williams discusses the hazards of laser interference with pilots. He recounts an episode in mid-July 2017 where he and a co-pilot were lased. They identified the source of the laser beam. Ground officers found that the perpetrator was a teenager. Williams said “We specifically requested that the cops not get the FBI involved. I don’t want any kids going to jail or getting felony charges on their record.”
He added, “When the cop showed up at the door and explained to the dad what was going on, the dad broke the kid’s laser there on the spot.”
The reluctance to report appears to stem from a 2009 lasing incident which was reported to the FBI. A 30-year-old man, Joshua Don Park, “on a whim” decided to aim a cat laser pointer at a Utah National Guard helicopter. Park told arresting officers that he was unaware the laser’s light could interfere with pilots’ operations. The Journal story says Park “faced up to five years in prison. [Another source says he faced up to 20 years.] Tragically, he committed suicide shortly before he could be sentenced.”
The story continues, “Since that sobering incident, no Utah National Guard pilots have reported lasing incidents to the FBI—but not for lack of occurrences. ‘My unit alone has had two incidents in the past three months,’ said Williams.”
From the South Valley Journal. More details about the original February 2009 lasing and September 2009 suicide are here.
In an interview, Chief Warrant Officer Robert Williams discusses the hazards of laser interference with pilots. He recounts an episode in mid-July 2017 where he and a co-pilot were lased. They identified the source of the laser beam. Ground officers found that the perpetrator was a teenager. Williams said “We specifically requested that the cops not get the FBI involved. I don’t want any kids going to jail or getting felony charges on their record.”
He added, “When the cop showed up at the door and explained to the dad what was going on, the dad broke the kid’s laser there on the spot.”
The reluctance to report appears to stem from a 2009 lasing incident which was reported to the FBI. A 30-year-old man, Joshua Don Park, “on a whim” decided to aim a cat laser pointer at a Utah National Guard helicopter. Park told arresting officers that he was unaware the laser’s light could interfere with pilots’ operations. The Journal story says Park “faced up to five years in prison. [Another source says he faced up to 20 years.] Tragically, he committed suicide shortly before he could be sentenced.”
The story continues, “Since that sobering incident, no Utah National Guard pilots have reported lasing incidents to the FBI—but not for lack of occurrences. ‘My unit alone has had two incidents in the past three months,’ said Williams.”
From the South Valley Journal. More details about the original February 2009 lasing and September 2009 suicide are here.
UK: Police get advice from U.S. FBI on stopping U.K. laser incidents
13 Jul 2014 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Statistics | Finding perpetrators | Laws | SLA news | Ways to reduce incidents
In May 2014, U.K. police officials met with U.S. FBI agents in Washington DC, to gain insights into how to reduce the almost 2,000 laser/aircraft incidents reported in 2013. According to a report in the Express, British police said they do not have sufficient investigatory powers, that it is hard to get convictions, and that the only punishment is minor fines.
While both the U.S. and the U.K. have laws with penalties up to five years in jail, in the States jail sentences have been imposed while fines are the norm in Britain. The U.S. also has a centralized national reporting system, which the British officials seek to emulate.
Mark Callaghan, an NPT inspector for Sussex Police, told the Express about a case in April 2014 where a laser beam was aimed at an Airbus A319 from a Travelodge near Gatwick Airport. The pilots reported that “The green laser was extremely aggressive and we suffered three or four two-second attacks directly into the cockpit causing blotchy vision, squinting, broken concentration, sore eyes.” The perpetrators were not caught.
Callaghan noted “We can find out who was in the rooms but we have no power to conduct any searches and even if there were lasers there what evidence is there to say they did it? We would like some preventative legislation. The US have got it nailed on how they deal with this.”
From the Express
While both the U.S. and the U.K. have laws with penalties up to five years in jail, in the States jail sentences have been imposed while fines are the norm in Britain. The U.S. also has a centralized national reporting system, which the British officials seek to emulate.
Mark Callaghan, an NPT inspector for Sussex Police, told the Express about a case in April 2014 where a laser beam was aimed at an Airbus A319 from a Travelodge near Gatwick Airport. The pilots reported that “The green laser was extremely aggressive and we suffered three or four two-second attacks directly into the cockpit causing blotchy vision, squinting, broken concentration, sore eyes.” The perpetrators were not caught.
Callaghan noted “We can find out who was in the rooms but we have no power to conduct any searches and even if there were lasers there what evidence is there to say they did it? We would like some preventative legislation. The US have got it nailed on how they deal with this.”
From the Express
US: Wall Street Journal article describes laser pointer hazards to aircraft
The Wall Street Journal published a story August 27 2014, by legal reporter Ashby Jones, entitled “Laser-Pointer Strikes Menace Pilots: Jail Sentences, Rewards Haven’t Stopped the Practice.”
The article begins by saying that “People keep aiming powerful laser pointers at aircraft ... despite jail sentences for offenders and rewards for people who turn them in.”
It quotes unnamed law enforcement experts and prosecutors as saying that most strikes are “not done out of maliciousness, but irresponsibility.” The FAA told the WSJ author that no accidents or aborted takeoffs or landings have been attributed to laser incidents.
Jones notes that the FBI’s recent publicity and prosecution campaign “appear[s] to have led to some success, with the number of laser strikes in recent months dropping to about nine a day from about 11 in 2013, according to an FBI spokeswoman. She said this crime was the first for which the FBI has offered a reward that didn’t involve a fugitive or missing person.”
The article describes a few cases, then in the penultimate paragraph, states “Still, thousands of laser strikes, particularly involving commercial planes, go unpunished. Since 2005, only 162 people have been arrested for strikes, and 86 convicted, according to the FBI.”
From the Wall Street Journal. The article may be behind a paywall, requiring a subscription to access the full text. Aviation reporter Christine Negroni was moved by the WSJ article to respond a day later with a blog post entitled “Aviation’s Effort Combating Laser Attacks Hashtag #Ineffective #Insane”.”
The article begins by saying that “People keep aiming powerful laser pointers at aircraft ... despite jail sentences for offenders and rewards for people who turn them in.”
It quotes unnamed law enforcement experts and prosecutors as saying that most strikes are “not done out of maliciousness, but irresponsibility.” The FAA told the WSJ author that no accidents or aborted takeoffs or landings have been attributed to laser incidents.
Jones notes that the FBI’s recent publicity and prosecution campaign “appear[s] to have led to some success, with the number of laser strikes in recent months dropping to about nine a day from about 11 in 2013, according to an FBI spokeswoman. She said this crime was the first for which the FBI has offered a reward that didn’t involve a fugitive or missing person.”
The article describes a few cases, then in the penultimate paragraph, states “Still, thousands of laser strikes, particularly involving commercial planes, go unpunished. Since 2005, only 162 people have been arrested for strikes, and 86 convicted, according to the FBI.”
From the Wall Street Journal. The article may be behind a paywall, requiring a subscription to access the full text. Aviation reporter Christine Negroni was moved by the WSJ article to respond a day later with a blog post entitled “Aviation’s Effort Combating Laser Attacks Hashtag #Ineffective #Insane”.”
US: UPDATED - Reporter questions effect of FAA/FBI "blame and shame" campaign
29 Aug 2014 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Arrests | Fines & Jail | Media and press | Ways to reduce incidents | Updated story | SLA news
A well-known aviation reporter has taken issue with how the FAA and FBI are trying to reduce the number of laser illuminations on aircraft. On August 28 2014, Christine Negroni published a post on her blog Flying Lessons entitled “Aviation’s Effort Combating Laser Attacks Hashtag #Ineffective #Insane”.
She disagrees with the U.S. government’s primary focus being a “blame and shame” campaign that tries to capture laser perpetrators using helicopters, then prosecutes them and publicizes the resulting multi-year sentences. Negroni calls this a “high-tech, heavy-metal, dollar-intensive approach to the problem … [that] has gone terribly wrong…”
Her contention is that persons who aim at aircraft “don’t watch television news, read the daily newspaper or log on to the FAA laser education website before heading out into the night with their nifty green or blue laser pointers.”
She ends her blog post by calling for creativity to try to market this message to its target audience of teens and young men, using a more sophisticated publicity or social media effort.
In the past few years Negroni has written about what she calls “this disaster in the making” for the New York Times, MSNBC, and the Smithsonian’s Air & Space magazine. Late in 2013, she wrote a more detailed article for the blog Runway Girl Network, exploring the problem — and suggested solutions — in more depth.
From Flying Lessons. Background information disclosure: LaserPointerSafety.com provided some information to Negroni which was used in her articles.
UPDATED September 8 2014 - Negroni’s blog post was reprinted by the Huffington Post.
She disagrees with the U.S. government’s primary focus being a “blame and shame” campaign that tries to capture laser perpetrators using helicopters, then prosecutes them and publicizes the resulting multi-year sentences. Negroni calls this a “high-tech, heavy-metal, dollar-intensive approach to the problem … [that] has gone terribly wrong…”
Her contention is that persons who aim at aircraft “don’t watch television news, read the daily newspaper or log on to the FAA laser education website before heading out into the night with their nifty green or blue laser pointers.”
She ends her blog post by calling for creativity to try to market this message to its target audience of teens and young men, using a more sophisticated publicity or social media effort.
In the past few years Negroni has written about what she calls “this disaster in the making” for the New York Times, MSNBC, and the Smithsonian’s Air & Space magazine. Late in 2013, she wrote a more detailed article for the blog Runway Girl Network, exploring the problem — and suggested solutions — in more depth.
From Flying Lessons. Background information disclosure: LaserPointerSafety.com provided some information to Negroni which was used in her articles.
UPDATED September 8 2014 - Negroni’s blog post was reprinted by the Huffington Post.
US: FAA-reported laser incidents decline 12.8% compared to 2013
According to statistics furnished by the Federal Bureau of Investigation, laser incidents in the U.S. average 9.5 per night for the period January 1 to August 7, 2014. This compares with 10.8 incidents per night in all of 2013, and is equal to 2012’s year-long average of 9.5 per night.
During the 219 days from January 1 to August 7, 2014, there were 2,085 laser incidents reported to the Federal Aviation Administration, according to the FBI data. This is a 12.8% reduction compared with 2,390 incidents during the same 219-day period in 2013, and is an 8% increase compared with 1,925 incidents Jan. 1- Aug. 7, 2012.
One reason for the decline may be the FBI’s campaign to prosecute offenders, and to inform the public via press releases and public service announcements that it is illegal to aim a laser at aircraft.
Based on the Jan-Aug 2014 data, the number of illuminations in 2014 is expected to fall below 3,500.
During the 219 days from January 1 to August 7, 2014, there were 2,085 laser incidents reported to the Federal Aviation Administration, according to the FBI data. This is a 12.8% reduction compared with 2,390 incidents during the same 219-day period in 2013, and is an 8% increase compared with 1,925 incidents Jan. 1- Aug. 7, 2012.
One reason for the decline may be the FBI’s campaign to prosecute offenders, and to inform the public via press releases and public service announcements that it is illegal to aim a laser at aircraft.
Based on the Jan-Aug 2014 data, the number of illuminations in 2014 is expected to fall below 3,500.
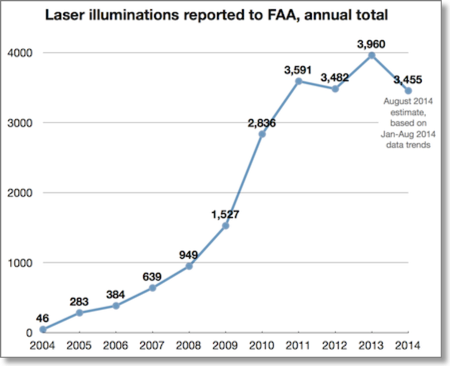
From information provided to LaserPointerSafety.com, and analysis of FAA data for previous years. For 2013 and past years’ data, see the page FAA laser/aircraft incidents: 2004-2013 historical data
US: FBI expands laser education & reward campaign nationwide for 3 months
03 Jun 2014 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Finding perpetrators | Media and press | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
The FBI is expanding nationwide its program to publicize the hazards of aiming laser pointers at aircraft, and to offer up to $10,000 as a reward for information leading to the arrest of laser perpetrators.
The original FBI education and reward program ran from February 11 to April 11 2014 in 12 U.S. cities that had high rates of laser/aircraft incidents. The FBI said the program led to a 19 percent decrease in lasing reports.
The new, nationwide program was announced June 3 2014. The $10,000 reward offer is scheduled to last for 90 days; until September 1.
The FBI said they are working on the educational campaign with the Federal Aviation Administration, the Air Line Pilots Association, International, and state, local and international law enforcement. They are outreaching to schools, teaching teens to not aim at aircraft.
Click to read more...
The original FBI education and reward program ran from February 11 to April 11 2014 in 12 U.S. cities that had high rates of laser/aircraft incidents. The FBI said the program led to a 19 percent decrease in lasing reports.
The new, nationwide program was announced June 3 2014. The $10,000 reward offer is scheduled to last for 90 days; until September 1.
The FBI said they are working on the educational campaign with the Federal Aviation Administration, the Air Line Pilots Association, International, and state, local and international law enforcement. They are outreaching to schools, teaching teens to not aim at aircraft.
Click to read more...
US: 134 laser arrests, 80 convictions, out of 17,725 incidents, 2005-2013
21 May 2014 -- Categories: Statistics | Fines & Jail | Arrests | Finding perpetrators | Laws | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
According to Ars Technica writer Cyrus Farivar, in the U.S. from 2005 to 2013 there were 134 arrests for aiming lasers at aircraft, out of 17,725 FAA-reported lasing incidents. He wrote “That means that even amongst reported incidents, there’s only a 0.75 percent chance of getting caught. Adding countless unreported incidents would only make that minuscule percentage go down further.”
Farivar noted that there were 80 convictions among the 134 arrests. One reason for the conviction rate of 60%: some who were arrested were minors who were never formally charged.
The extensively researched 4,200-word article, dated May 21 2014, was based around the 14-year sentence handed down in March 2014 to Sergio Rodriguez, for his August 2012 aiming of a laser at two helicopters, one medical and one police. Farivar used the case to illustrate many laser/aviation issues, especially about how prosecution is being used to try to educate and deter future incidents.
Farivar interviewed Karen Escobar, who has brought more cases against laser perpetrators than any other federal prosecutor. Her territory includes Sacramento, Fresno, and Bakersfield.
In the article, Escobar was quoted as saying “At sentencing, [Rodriguez] did not accept responsibility for his actions; he blamed his 2- and 3- year-old children. I believe the evidence showed the laser was a dangerous weapon, and there was intention, supporting a guideline sentence of 168 months. I would not call it harsh. I would say it is a penalty that fits the crime, but I believe that it will have a deterrent effect, and I hope it will.”
Farivar noted that, “While 14 years might sound incredibly excessive for an incident that caused no serious or lasting physical injury, much less death, this is the emerging reality for attorneys prosecuting laser strikes. The Rodriguez sentence now serves as an example of what can happen to defendants who don't take plea deals. (The plea deals typically end up being around two years.)”
From Ars Technica
Farivar noted that there were 80 convictions among the 134 arrests. One reason for the conviction rate of 60%: some who were arrested were minors who were never formally charged.
The extensively researched 4,200-word article, dated May 21 2014, was based around the 14-year sentence handed down in March 2014 to Sergio Rodriguez, for his August 2012 aiming of a laser at two helicopters, one medical and one police. Farivar used the case to illustrate many laser/aviation issues, especially about how prosecution is being used to try to educate and deter future incidents.
Farivar interviewed Karen Escobar, who has brought more cases against laser perpetrators than any other federal prosecutor. Her territory includes Sacramento, Fresno, and Bakersfield.
In the article, Escobar was quoted as saying “At sentencing, [Rodriguez] did not accept responsibility for his actions; he blamed his 2- and 3- year-old children. I believe the evidence showed the laser was a dangerous weapon, and there was intention, supporting a guideline sentence of 168 months. I would not call it harsh. I would say it is a penalty that fits the crime, but I believe that it will have a deterrent effect, and I hope it will.”
Farivar noted that, “While 14 years might sound incredibly excessive for an incident that caused no serious or lasting physical injury, much less death, this is the emerging reality for attorneys prosecuting laser strikes. The Rodriguez sentence now serves as an example of what can happen to defendants who don't take plea deals. (The plea deals typically end up being around two years.)”
From Ars Technica
US: FBI offers $10,000 reward; warns public about laser pointer misuse
11 Feb 2014 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Finding perpetrators | Media and press | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
For 60 days, the Federal Bureau of Investigation is offering a reward of $10,000 for information about anyone pointing a laser at an aircraft. Between February 11 and April 11 2014, persons reporting lasers being pointed at aircraft should call their local FBI field office or the 911 emergency number.
This comes as part of a publicity campaign by the FBI to inform the public and especially teenagers about the dangers of lasing aircraft. The agency said teens are the primary age group responsible for laser/aircraft illuminations.
[Note: There appear to be no official records of perpetrators’ ages. However, here are lists of incidents recorded in LaserPointerSafety.com news items, based on the age of the perpetrator: 10-19, 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59, 60-69. Counting the stories in each group may give a rough indication of the age distribution of laser perpetrators.]
The two-month campaign will focus on 12 cities with large number of incidents. FBI field offices participating in the regional reward program are Albuquerque, Chicago, Cleveland, Houston, Los Angeles, New York City, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Sacramento, San Antonio, San Juan, and the Washington Field Office.
During the campaign, the FBI and the Air Line Pilots Association International will work with Clear Channel Outdoor to hang billboards and issue public service announcements in these cities, warning people that a laser prank can lead to prison.
Click to read more...
This comes as part of a publicity campaign by the FBI to inform the public and especially teenagers about the dangers of lasing aircraft. The agency said teens are the primary age group responsible for laser/aircraft illuminations.
[Note: There appear to be no official records of perpetrators’ ages. However, here are lists of incidents recorded in LaserPointerSafety.com news items, based on the age of the perpetrator: 10-19, 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59, 60-69. Counting the stories in each group may give a rough indication of the age distribution of laser perpetrators.]
The two-month campaign will focus on 12 cities with large number of incidents. FBI field offices participating in the regional reward program are Albuquerque, Chicago, Cleveland, Houston, Los Angeles, New York City, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Sacramento, San Antonio, San Juan, and the Washington Field Office.
During the campaign, the FBI and the Air Line Pilots Association International will work with Clear Channel Outdoor to hang billboards and issue public service announcements in these cities, warning people that a laser prank can lead to prison.
Click to read more...
US: NIST working to get forensics labs to measure laser pointers for court cases
The National Institute of Standards and Technology is working with law enforcement to measure the actual power and divergence of laser pointers used against aircraft. NIST hopes to develop a Hand-Held Laser Characterization System for about $10,000 to $30,000 which can be used in FBI or police forensics labs. This will help in prosecution of cases of lasers illegally aimed at aircraft.
The effort began when NIST physicist and laser safety officer Joshua Hadler worked with the U.S. Attorney’s office on a 2013 case in Fresno, California. Hadler already had devised a relatively simple and inexpensive way to accurately measure laser pointer powers. (His widely-reported study showed that a majority of pointers exceeded the U.S. limit of 5 milliwatts.)
But power is only one factor of the potential laser hazard. The beam spread, or divergence is another key factor. This is because a wide, high-divergence beam will have its energy spread out more, making it dimmer and less hazardous at a distance than an otherwise equivalent-power laser with a narrower, low-divergence beam.
To tackle this, Hadler used a pyroelectric laser camera to measure the laser’s divergence. From the power and divergence, and knowing the approximate distance to the aircraft from the Federal Aviation Administration incident reports, Hadler was able to calculate the irradiance, or laser power over a given area.
The information helped to get a conviction in the Fresno case. Hadler noted that in the past, “...the vast majority of prosecutions were failing, due in no small part to a basic lack of knowledge about the laser devices on the part of nearly everyone in the trial process, including lawyers, judges, and jury members. What they needed was to be able to acquire and present quantitative data about a device's power and its effects at a specified range that could be used in the judicial process."
Hadler will present a paper on February 21 2014 at the American Academy of Forensic Sciences meeting in Seattle, Washington. The paper, “Output Characterization of Handheld Lasers Used in Criminal Aircraft Illumination,” will discuss the needed measurements and will present ideas for having these measurements be done outside of NIST, in law enforcement forensic labs.
From PhysOrg
The effort began when NIST physicist and laser safety officer Joshua Hadler worked with the U.S. Attorney’s office on a 2013 case in Fresno, California. Hadler already had devised a relatively simple and inexpensive way to accurately measure laser pointer powers. (His widely-reported study showed that a majority of pointers exceeded the U.S. limit of 5 milliwatts.)
But power is only one factor of the potential laser hazard. The beam spread, or divergence is another key factor. This is because a wide, high-divergence beam will have its energy spread out more, making it dimmer and less hazardous at a distance than an otherwise equivalent-power laser with a narrower, low-divergence beam.
To tackle this, Hadler used a pyroelectric laser camera to measure the laser’s divergence. From the power and divergence, and knowing the approximate distance to the aircraft from the Federal Aviation Administration incident reports, Hadler was able to calculate the irradiance, or laser power over a given area.
The information helped to get a conviction in the Fresno case. Hadler noted that in the past, “...the vast majority of prosecutions were failing, due in no small part to a basic lack of knowledge about the laser devices on the part of nearly everyone in the trial process, including lawyers, judges, and jury members. What they needed was to be able to acquire and present quantitative data about a device's power and its effects at a specified range that could be used in the judicial process."
Hadler will present a paper on February 21 2014 at the American Academy of Forensic Sciences meeting in Seattle, Washington. The paper, “Output Characterization of Handheld Lasers Used in Criminal Aircraft Illumination,” will discuss the needed measurements and will present ideas for having these measurements be done outside of NIST, in law enforcement forensic labs.
From PhysOrg
US: FBI uses sophisticated surveillance to catch Portland man who lased ~25 aircraft
Multiple police and government agencies, led by the FBI, flew airplanes and installed surveillance cameras, in a sophisticated attempt to find the person who had aimed a laser pointer at aircraft over 25 times. The story, which reads like a spy novel, is laid out in an application for a search warrant that was filed by the FBI October 17 2013 with the U.S. District Court for the District of Oregon.
The operation was initiated in August 2013, after multiple incidents of lasers being aimed at aircraft around Portland International Airport. Four law enforcement aircraft were equipped with video surveillance cameras.
On August 10, five aircraft were targeted by a ground-based green laser. One was an Alaska Airlines flight; two were from the FBI and two were from the Portland Police Bureau. At the same time, a surveillance team was on the ground. Using information from the FBI/PBB aircraft sightings, the ground officers observed suspicious behavior from a male in the back yard of a duplex apartment. He was looking up at the sky. He removed something mounted from a stand or pole, and went inside. The laser strikes ceased afterwards.
Six days later, after reviewing the video, consulting Google Earth and Google Maps, and visiting the apartment complex, an FBI Special Agent determined that Apartment 35 -- the one previously surveilled -- was the most likely source of the laser. The apartment was occupied by 39-year-old Stephen Francis Bukucs.
Surveillance cameras were then secretly installed, watching Apartment 35. They could see in daylight, low light and nighttime (using infrared).
Click to read more...
The operation was initiated in August 2013, after multiple incidents of lasers being aimed at aircraft around Portland International Airport. Four law enforcement aircraft were equipped with video surveillance cameras.
On August 10, five aircraft were targeted by a ground-based green laser. One was an Alaska Airlines flight; two were from the FBI and two were from the Portland Police Bureau. At the same time, a surveillance team was on the ground. Using information from the FBI/PBB aircraft sightings, the ground officers observed suspicious behavior from a male in the back yard of a duplex apartment. He was looking up at the sky. He removed something mounted from a stand or pole, and went inside. The laser strikes ceased afterwards.
Six days later, after reviewing the video, consulting Google Earth and Google Maps, and visiting the apartment complex, an FBI Special Agent determined that Apartment 35 -- the one previously surveilled -- was the most likely source of the laser. The apartment was occupied by 39-year-old Stephen Francis Bukucs.
Surveillance cameras were then secretly installed, watching Apartment 35. They could see in daylight, low light and nighttime (using infrared).
Click to read more...
US: New York area officials ask for public's help
At a September 20 2012 press conference at New Jersey State Police Headquarters, officials from the New York tri-state area asked the public’s help in identifying persons who aim lasers at aircraft. Such incidents occur about once per day at airports in the New York-New Jersey-Connecticut area.
A pilot from the Air Line Pilots Association told of his experiences when hit by laser light, and said that “Laser illumination can cause temporary blindness and even permanently damage a pilot’s eyes, potentially leading to an aircraft accident…Individuals must understand the danger and their responsibility to report anyone who misuses lasers.”
The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey is sending officers to schools near airports, to explain the hazards of lasers to children, and to warn them against aiming at aircraft.
An FBI agent said that the bureau is worried about adults and deliberate attacks by terrorists. Fines can range up to $11,000, said an FAA representative. a Coast Guard pilot said that rules requiring helicopters to break off rescues if they are directly lasered, adds to the risk of those the Coast Guard is trying to rescue.
The various law enforcement officials said they were asking the public to call 911 or local authorities if they see misuse, because laser incidents are so frequent and it is rare to apprehend the perpetrators.
A radio station public service announcement has been produced and aired by radio station NJ 101.5. It warns listeners not to aim at aircraft.
From NBC New York and New Jersey 101.5
A pilot from the Air Line Pilots Association told of his experiences when hit by laser light, and said that “Laser illumination can cause temporary blindness and even permanently damage a pilot’s eyes, potentially leading to an aircraft accident…Individuals must understand the danger and their responsibility to report anyone who misuses lasers.”
The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey is sending officers to schools near airports, to explain the hazards of lasers to children, and to warn them against aiming at aircraft.
An FBI agent said that the bureau is worried about adults and deliberate attacks by terrorists. Fines can range up to $11,000, said an FAA representative. a Coast Guard pilot said that rules requiring helicopters to break off rescues if they are directly lasered, adds to the risk of those the Coast Guard is trying to rescue.
The various law enforcement officials said they were asking the public to call 911 or local authorities if they see misuse, because laser incidents are so frequent and it is rare to apprehend the perpetrators.
A radio station public service announcement has been produced and aired by radio station NJ 101.5. It warns listeners not to aim at aircraft.
From NBC New York and New Jersey 101.5
US: ALPA holds major D.C. conference on the threat of laser illuminations
31 Oct 2011 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Eye effect or injury | Statistics | Laws | Media and press | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
An all-day conference in Washington D.C. brought together legislators, regulators, aviation safety officials and pilots to discuss "Laser Illumination of Aircraft: A Growing Threat." The October 27 2011 event was organized by ALPA, the Air Line Pilots Association. It was primarily intended to bring public attention to the many aspects of this issue. (Selected presentations are available from the ALPA laser conference website.)
Speakers generally agreed on the nature and scope of lasers as a threat to air safety. They also offered similar solutions, including educating the public to not misuse lasers, prosecuting those who do, training pilots on how to "recognize and recover" from incidents, increasing the number of reports from pilots and the public, and restricting laser pointer availability.
The ALPA conference made news primarily for the announcement of a new FAA web page, which can be reached via www.faa.gov/go/laserinfo. FAA Administrator Randy Babbitt told the ALPA attendees that the web page -- erroneously described as a "website" in many media accounts -- would centralize the agency's information on laser/aviation safety. The page includes email addresses where pilots, air traffic control and the public can report laser incidents (see separate story about the FAA web page).
Babbitt also said that the FAA currently has filed 18 civil cases against individuals who aimed lasers at aircraft. There is a maximum $11,000 fine in each case.
Other speakers gave updates and information in their areas of expertise.Click to read more...
Speakers generally agreed on the nature and scope of lasers as a threat to air safety. They also offered similar solutions, including educating the public to not misuse lasers, prosecuting those who do, training pilots on how to "recognize and recover" from incidents, increasing the number of reports from pilots and the public, and restricting laser pointer availability.
The ALPA conference made news primarily for the announcement of a new FAA web page, which can be reached via www.faa.gov/go/laserinfo. FAA Administrator Randy Babbitt told the ALPA attendees that the web page -- erroneously described as a "website" in many media accounts -- would centralize the agency's information on laser/aviation safety. The page includes email addresses where pilots, air traffic control and the public can report laser incidents (see separate story about the FAA web page).
Babbitt also said that the FAA currently has filed 18 civil cases against individuals who aimed lasers at aircraft. There is a maximum $11,000 fine in each case.
Other speakers gave updates and information in their areas of expertise.Click to read more...
US: Two FBI videos warning against lasers get 250,000+ YouTube views
29 Sep 2011 -- Categories: Aviation incidents | Labels and warnings | Media and press | Ways to reduce incidents | SLA news
The FBI issued a press release and YouTube video on September 26 2011, warning the public against aiming lasers at aircraft. Titled “Making a Point about Lasers”, the informational video garnered over 25,000 views on YouTube in three days:
The video highlights Justin Stouder, a St. Louis-area resident who was arrested in April 2010 for aiming at a police helicopter. He apologized at a news conference in July 2011 intended to publicize the illegality and hazards of lasers aimed at aircraft.
The FBI also released video excerpts of the Stouder laser incident and his subsequent identification by the helicopter and arrest. The incident/arrest video was about 10 times as popular on YouTube, with over 225,000 views:
The press release, and a transcript of the video, are below (click on the Read More… link).Click to read more...
The video highlights Justin Stouder, a St. Louis-area resident who was arrested in April 2010 for aiming at a police helicopter. He apologized at a news conference in July 2011 intended to publicize the illegality and hazards of lasers aimed at aircraft.
The FBI also released video excerpts of the Stouder laser incident and his subsequent identification by the helicopter and arrest. The incident/arrest video was about 10 times as popular on YouTube, with over 225,000 views:
The press release, and a transcript of the video, are below (click on the Read More… link).Click to read more...
US: 3 sheriff's officers charged with illegal laser sales
Three officers in the Lake County (Indiana) Sheriff’s Department were indicted for illegally reselling laser sights and machine gun parts that are restricted for law enforcement use only. The officers resigned, accepted responsibility, and entered into a plea agreement announced September 22 2011.
92 laser sights and 74 automatic machine guns were ordered between Sept. 2008 and January 2010 on Lake County letterhead and purchase orders. The officers paid for the products with personal funds. The amount earned from Internet resales was not stated, although the three officers were also indicted for understating their personal income by a total of $387,000.
The laser products came from Insight Technology Inc. and Laser Devices Inc. The 92 restricted laser sights were purchased for approximately $1000 to $1400 each and were sold on eBay for around $2800 to $4200 each. A special agent of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (which regulates laser devices) made an undercover purchase as part of the evidence-gathering process in the case.Click to read more...
92 laser sights and 74 automatic machine guns were ordered between Sept. 2008 and January 2010 on Lake County letterhead and purchase orders. The officers paid for the products with personal funds. The amount earned from Internet resales was not stated, although the three officers were also indicted for understating their personal income by a total of $387,000.
The laser products came from Insight Technology Inc. and Laser Devices Inc. The 92 restricted laser sights were purchased for approximately $1000 to $1400 each and were sold on eBay for around $2800 to $4200 each. A special agent of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (which regulates laser devices) made an undercover purchase as part of the evidence-gathering process in the case.Click to read more...
US: FBI to use laser event recorders in cockpits
15 Jun 2010 -- Categories: Finding perpetrators | SLA news
From a press release issued June 15, 2010 by Optra, Inc.:
OPTRA Inc. Awarded Purchase Contract by U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation to supply Laser Event Recorders
Topsfield, MA (June 15, 2010) - OPTRA Inc. was awarded a contract by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) to supply Laser Event Recorders (LER). The LERs will be used to fight the laser dazzle problem that has become an increasing problem for pilots worldwide in recent years.
The problem that pilots have been facing in increasing numbers is from people on the ground that point hand held laser devices at aircraft. Some of these lasers have a range of up to 5 miles and in some cases can cause temporary blindness for the pilot that could result in loss of control of the aircraft. With the LER being used in the cockpit of an aircraft it is possible to detect a laser pointed in the direction of an aircraft and allow the pilot to avoid eye contact while at the same time capturing critical information that can be used to locate, apprehend and prosecute the offender.
Click to read more...
OPTRA Inc. Awarded Purchase Contract by U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation to supply Laser Event Recorders
Topsfield, MA (June 15, 2010) - OPTRA Inc. was awarded a contract by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) to supply Laser Event Recorders (LER). The LERs will be used to fight the laser dazzle problem that has become an increasing problem for pilots worldwide in recent years.
The problem that pilots have been facing in increasing numbers is from people on the ground that point hand held laser devices at aircraft. Some of these lasers have a range of up to 5 miles and in some cases can cause temporary blindness for the pilot that could result in loss of control of the aircraft. With the LER being used in the cockpit of an aircraft it is possible to detect a laser pointed in the direction of an aircraft and allow the pilot to avoid eye contact while at the same time capturing critical information that can be used to locate, apprehend and prosecute the offender.
Click to read more...