Home
A comprehensive resource for safe and responsible laser use
US: New technique for scattering laser light on aircraft windscreens
The research was presented by Jason Keleher, Ph.D. and research assistant Daniel Maurer on March 31 2019 at an American Chemical Society meeting in Orlando, Florida. Here is a summary:
"To develop their new approach, the researchers took advantage of liquid crystals -- materials with properties between those of liquids and solid crystals that make them useful in electronic displays. The team placed a solution of liquid crystals called N-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-4-butylaniline (MBBA) between two 1-inch-square panes of glass. MBBA has a transparent liquid phase and an opaque crystalline phase that scatters light. By applying a voltage to the apparatus, the researchers caused the crystals to align with the electrical field and undergo a phase change to the more solid crystalline state.

Liquid crystals sandwiched between two1-inch squares of glass (left images) scatter green and blue light on a wall when the cells are triggered by laser illumination (right images). Image credit: Daniel Maurer, Lewis University
"The aligned crystals blocked up to 95 percent of red, blue and green beams, through a combination of light scattering, absorption of the laser's energy and cross-polarization. The liquid crystals could block lasers of different powers, simulating various distances of illumination, as well as light shone at different angles onto the glass.
"In addition, the system was fully automatic: A photoresistor detected laser light and then triggered the power system to apply the voltage. When the beam was removed, the system turned off the power, and the liquid crystals returned to their transparent, liquid state. "We only want to block the spot where the laser is hitting the windshield and then have it quickly go back to normal after the laser is gone," Keleher notes. The rest of the windshield, which was not hit by the laser, would remain transparent at all times.
"Now that the researchers have shown that their approach works, they plan to scale it up from 1-inch squares to the size of an entire aircraft windshield. Initial results have shown that a sensor grid pattern on 2-inch squares of glass will respond only to the section of glass that is illuminated. The team is also testing different types of liquid crystals to find even more efficient and versatile ones that return to the transparent state more quickly once the laser is removed."
Canada: Satair, Metamaterials sign anti-laser glare protection distribution deal
Customers will include commercial and military pilots, both fixed-wing and rotary, in markets including commercial aviation, business aviation, search and rescue, police, medevac and military.
Satair is a part of the Airbus Customer Services unit. In 2014 Airbus brought Nova Scotia-based MTI into an innovation start-up program, working to commercialize aircraft windscreen film to protect pilots from laser glare and flashblindness. In June 2017 Satair and MTI signed a memorandum of understanding focused on the civil aviation market.
According to MTI, "Detailed market research and discussions with potential customers since then has confirmed that the overwhelming preference is for this innovative new product to be introduced to the market through individual eyewear and visor products which incorporate MTI’s laser glare protection technology."

MTI's George Palikaras, founder and CEO (l), and Satair CEO Bart Reijnen (r) sign a distribution agreement at the October 2018 MRO Europe trade show for maintenance, repair and overhaul operations.
The October 2018 agreement widens the market and covers "eyewear and visor products that are developed or manufactured by MTI. These include, without limitation, all sub-components, sub-assemblies, piece parts, software and hardware."
MTI says their technology "is superior to other products currently on the market due to a unique and patented dielectric (non-metallic) optical metamaterial filter, which has been scientifically engineered to ensure that the pilots’ vision and interpretation of the surrounding environment is not disturbed during critical phases of flight."
From an October 17 2018 Metamaterial Technologies Inc. press release
UPDATED: In a February 19 2019 press release, Satair's customer solutions director says initial product applications will appear in the first quarter of 2019. He also said "The technology is highly scalable so it can be customised for a wide variety of platforms and other applications. In commercial aviation the green laser poses the biggest threat because the human eye is more susceptible to the green wavelength. For military markets the red laser may be the largest threat. The advantage of the MTI product compared to other products in the market is that it can be customised to the wavelengths the customer wants to be protected against. As we have exclusive distribution rights across civil aviation, military and defence, we are open to do business with leading OEMs of products such as night vision goggles, head-up displays, helicopter and fighter pilot helmets and aircraft flight deck visors. Other products in the market do not have the same quality, the same level of protection and colour balance that we have.
Thanks to Peter Smith and Leon McLin for bringing the February 2019 press release to our attention.
US: Advisory committee recommends pilot procedures, training and glare protection
ARP6378™ has three main parts:
- A description of how lasers can interfere with pilots’ vision and operational performance, and how pilots can reduce adverse effects.
- A recommendation for pilot training, including exposure to safe, simulated laser light in a simulator or other realistic flying environment
- A description of Laser Glare Protection eyewear and windscreen film, with recommendations for whether and how to use these.
The document was developed by the SAE G10OL “Operational Laser” committee over a two-year period. It is available for purchase from SAE for $78. A three-page preview, which includes most of the Table of Contents except the appendices, is here.
From SAE ARP6378™, “Guidance on Mitigation Strategies Against Laser Illumination Effects”, published June 2 2018. Available from SAE.org.
Click to read more...
US: Coast Guard evaluating laser strike protection for cockpit use
The Coast Guard cannot use standard laser eye protection, such as is used in laboratories and industry, because it blocks too much light. One of the options the RDC is looking at is “a flexible optical filter that is reflective of lasers only and has just a slight tint, so it doesn’t interfere with the pilot’s visibility. The material can be applied to any transparent surface, such as the cockpit windshield, to deflect harmful laser beams and prevent them from reaching the inside of the cockpit.”
The chief of the Coast Guard’s Safety Program Management Division indicated eyewear or visors would be short-term solutions, and laser protective coatings for the aircraft would be a long-term solution.
According to Coast Guard information, “[o]nce finalized, the RDC findings will be integrated into an ongoing laser eye protection project the Office of Safety and Environmental Health is conducting in partnership with the Naval Aeromedical Research University in Dayton, Ohio, and the Air Force Research Laboratory at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio.”
From a February 21 2018 blog post from the U.S. Coast Guard. Click the “Read more” link for the full blog text. Thanks to George Palikaras for bringing this to our attention.
Click to read more...
UK: UPDATED - BAE Systems developing laser-reducing film for pilots; lab tests successful
According a September 12 2017 BAE press release, a “series of successful laboratory trials have proven our method is effective against a wide range of laser wavelengths.”
BAE researchers told LaserPointerSafety.com: “The film, when installed can be programmed with a number of critical wavelengths (typically three). This film can be upgraded at a later date by either replacing it entirely or adding on a new layer retrospectively to give protection against a new or emerging threat.”
They noted that the film has been measured as having 70% visible light transmission in a multi-wavelength blocking configuration.
The BAE film may be similar in general concept to another film from Metamaterial Technologies Inc. which has been tested by Airbus and is entering the production and deployment stages.
More information about anti-laser windscreen film in general and the MTI version specifically is here.
A press release from BAE is printed below. BAE also made available a graphic with similar information; click the blue “Click to read more…” link to see these.
UPDATED September 13 2017 —We reached out to BAE for additional details about their film; answers are after the press release and graphic.
Click to read more...
Canada: Laser protection windscreen film offered by Airbus subsidiary for civil aviation
Satair Group is a subsidiary of Airbus which offers parts management, service and support for all types of aircraft. Satair expects to receive a Supplemental Type Certificate from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration, the European Aviation Safety Agency, and Transport Canada Civil Aviation in early 2018. Other jurisdictions will follow.
The metaAIR film was invented and is manufactured by Metamaterial Technologies Inc. (MTI) of Halifax, Nova Scotia. The company previously worked with Airbus to evaluate, verify and test metaAIR for use in Airbus aircraft; initially for the A320 family. The Satair agreement will bring metaAIR to all commercial aircraft including Airbus and Boeing.
From a June 21 2017 MTI press release. For more details, click the link below for an interview with MTI’s George Palikaras, discussing the technology and this agreement.
Click to read more...
Canada: Airbus agrees to commercialize anti-laser windscreen material; eliminates need for laser protective eyewear
The film is not designed to fully block the laser light. It will significantly reduce the glare and temporary flash blindness effects that can occur when a laser is aimed at an aircraft cockpit. This in turn reduces the potential hazard of a laser illumination.
The announcement was made at a February 21 2017 press conference. In a press release kit photo, MTI’s founder and CEO, George Palikaras, demonstrated the laser-reflecting properties by holding up a windscreen that included MTI’s metaAIR film:
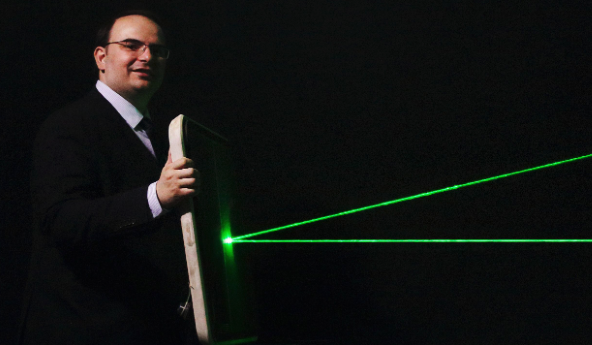
The press release did not indicate a time frame for introduction of the windscreens into service, nor details such as an estimated cost, or aircraft to be outfitted. An Airbus spokesperson did say that there are applications beyond the company’s commercial aircraft division. Palikaras said that metaAIR “can offer solutions in other industries including the military, transportation and glass manufacturers.”
For more detailed information on Airbus’ and MTI’s plans, see this page which includes interview Q&A questions with George Palikaras a few days after the February 21 press conference.
UPDATED April 14 2017: Metamaterials Technologies Inc. closed an $8.3 million round of funding. This will be used to support commercialization of the windscreen film and to add needed staff. MTI can produce metaAIR sheets 80 cm wide by 100 cm long, which is sufficient for standard cockpit windows that are 60 cm wide. However, the process is currently semi-automated and needs to be fully automated. MTI is also looking for new headquarters. From the Chronicle Herald.
UPDATED July 5 2017: MTI will be making its metaAIR anti-laser windscreen film available to non-Airbus aircraft, through aviation parts supplier Satair. An interview with George Palikaras goes into details.
Metamaterial Technologies Inc. issued a press release dated February 21 2017, which is reprinted below.
Click to read more...
US: Study shows windscreen coatings can reduce laser intensity
More information at the LaserPointerSafety.com page on the 2015 Nanocomposite coating study
Canada: UPDATED - Airbus to test windscreen anti-laser film
Lamda Guard’s “metaAir” film uses metamaterials, also called nano-composites, to reflect one or more laser colors without interfering with normal visibility. According to the company, the film can protect from beam angles up to +/- 50 degrees away from head-on. This has benefits when protecting cockpits against laser strikes, which can come from any angle.
It can be adhesively applied to glass or clear plastic; applications include eyewear, protective goggles and windscreens. Lamda Guard says that the Airbus tests on windscreens will mark the first time an optical metamaterial nano-composite has been applied on a large-scale surface.
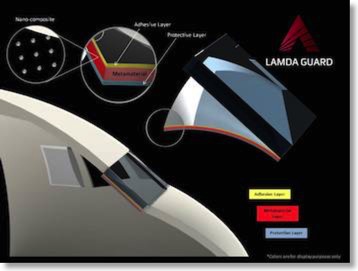
General schematic of metaAir film. Click for larger image.
The metaAir film can be engineered either to absorb or reflect the desired wavelength(s). For aircraft application, the reflection approach is being used in order to block undesired light wavelengths from entering the cockpit. The reflection bandwidth is currently in the 15-20 nanometer range.
For the most common type of green laser pointer -- responsible for 93% of FAA reported incidents in 2013 -- with a wavelength of 532 nm, the film would block light from about 522 to 542 nm. Additional wavelength blocking can be added as well, such as the 445 nm blue used in powerful handheld lasers such as the Wicked Lasers S3 Arctic that has up to 2 watts (2000 milliwatts) output.
Two key advantages of blocking laser light at the windscreen are that pilots do not have to carry or use laser protective eyewear, and there is absolutely no interference with the visibility of aircraft instruments. In preliminary tests, the anti-laser film had a narrow enough bandwidth that it did not interfere with airport lights seen outside a cockpit.
Because of ultraviolet degradation to the adhesive layer that adheres the optical metamaterial to the windscreen, the film would need to be replaced after about 5,000 flight hours. This translates into overnight replacement roughly once every three years. The optical metamaterial itself would not have a flight hour restriction.
In addition to piloted commercial aircraft windscreens, Airbus will also be investigating related applications such as piloted military windscreens, UAV camera protection, and sensor protection for satellites and airborne platforms.